B is an organic catalyst. As nouns the difference between enzyme and zymogen.
Enzymes What Are Enzymes Enzymes Are Ppt Download
An active site is where the enzymes substrates undergo a chemical reaction.

. This explains the main difference between enzyme and coenzyme. Would you expect a fat and a sugar molecule to be actedupon by the same enzyme. Enzymes the catalysts of biological systems are remarkable molecular devices that determine the pattern of chemical transformations.
Difference Between Catalyst and Enzyme Definition. Other common kinds of catalysts include acid-base catalysts and heterogeneous or surface catalysts. There is little difference in the size of catalyst and substrate molecules.
The crucial difference between Hormones and Enzymes is their chemical composition. Its concentration and composition remain unchanged. Although RNAs are capable of catalyzing some reactions most biological reactions are catalyzed by proteins.
Catalysts can be inorganic compounds. Enzymes are a class of catalysts that are responsible for facilitating and increasing. What is the main difference between a Pt catalyst and an enzyme catalyst.
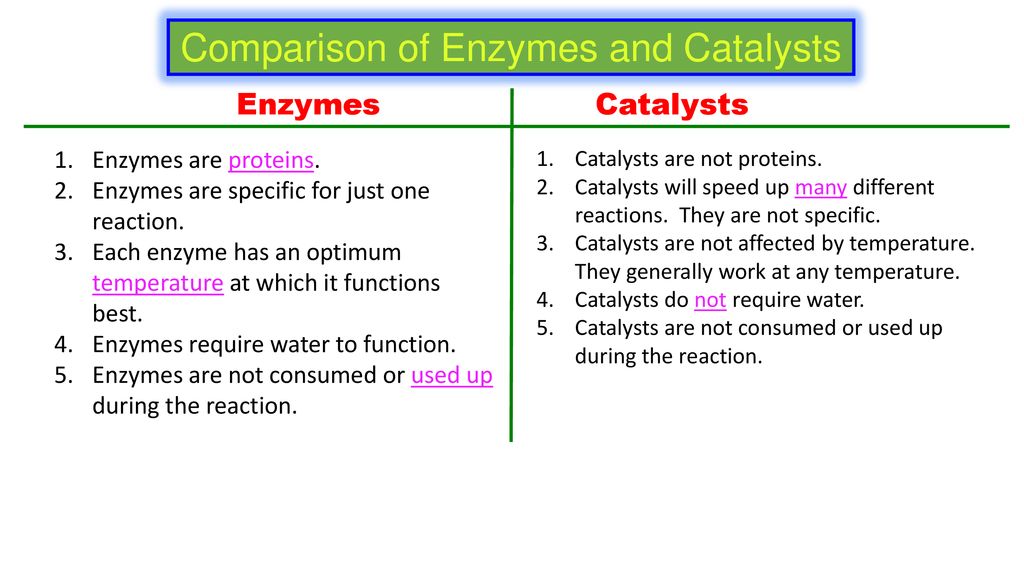
Neither catalysts nor enzymes are consumed in the reactions they catalyze. 13 rows Key Differences. It was a morning baptized by my first cup of coffee freshly brewed over a gravel-bar fire while they celebrated with the stronger catalyst of sour-mash whiskey in their.
A is a source of energy for endergonic reactions. D increasing the potential energy difference between reactant and product. Catalyst can be either inorganic catalysts or enzymes.
Explain the difference between a catalyst and an enzyme. B adding a phosphate group to a reactant. Catalysis is a phenomenon in which the rate of the reaction is altered with the help of a substance called a catalyst the catalyst does not participate in the reaction.
Enzymes are a type of a catalyst. Explain how an inhibitor can disrupt the action of an enzyme even if it doesnt bind to the enzymes active site. Enzyme molecules are organic biomolecules.
The globular proteins are called the enzymes whereas the small molecules or. Enzymes are a good example of biological catalysts. The difference between an enzyme and a hormone is that the enzyme is protein in nature and acts as a catalyst that increases the speed of the different reactions that take place in the body.
An inhibitor decreases reaction rates without affecting the stoichiometry. One of the major differences between enzymes and hormones is that enzymes act as a catalyst for a reaction and hormones act as messengers that trigger various functions in the body. What is the difference between a catalyst and enzyme.
What is an active site and what is its job. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any. The upcoming discussion will update you about the differences between Inorganic Catalysts and Enzymes.
The difference between catalysts and. E adding energy to a reaction. Would you expect a fat and a sugar molecule to be acted upon by the same enzyme.
They are inorganic in nature. Enzyme molecules are organic biomolecules. All enzymes are catalysts but not all catalysts are enzymes.
The substance used to change the rate of the reaction is called a catalyst. An enzyme refers to a substance produced by living organisms to act as a biological catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction while a coenzyme refers to a non-protein compound necessary for the functioning of an enzyme. What is the difference between a catalyst and an enzyme.
Are enzymes specific in theiraction. All enzymes are catalysts butnot all catalysts are enzymes. A fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymescatalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells.
Hormones are chemical messengers that transmit signals to. Many biochemical processes such as the oxidation of glucose are heavily dependent on enzymes proteins that behave as catalysts. Hence All enzymes are catalysts but not all.
Is that enzyme is biochemistry a globular protein that catalyses a biological chemical reaction while zymogen is biochemistry a proenzyme or enzyme precursor which requires a biochemical change ie hydrolysis to become an active form of the enzyme. There are two types of catalysts as homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts. An enzyme catalyst has greater substrate specificity.
In the absence of enzymatic catalysis most biochemical reactions are so slow that they would not occur under the mild conditions of. What isthe difference between a catalyst and an enzyme. Almost all known enzymes are proteins.
Up to 256 cash back 7. C can bind to nearly any molecule. Difference Inorganic Catalysts.
However in heterogeneous catalysts the molecules are in a different phase to that of reactant molecules. Explain why or why not. Explain the difference between competitive and noncompetitive inhibition.
A catalyst increases the reaction rates while not affecting the stoichiometry. Enzymes is that enzymes are largely organic in nature and are bio-catalysts while non-enzymatic. Catalysts are chemicals that depending on the type increase or decrease the rate of a chemical reaction but do not.
Answer The distinction between catalysts and enzymes is that enzymes are in large part natural in nature and are bio-catalysts. In homogeneous catalysts the molecules are in the same phase as reactant molecules. Enzymes are a type of catalyst found in only living things and Catalysts speed up a reaction.
Are enzymes specific in their action. Explain why or why not. Economic development and integration are working as a catalyst for peace.
Difference Between Catalyst And Enzyme Definition Characteristics Examples Comparison
Difference Between Catalyst And Enzyme Definition Characteristics Examples Comparison

0 Comments